Why do at least 70% of EHR implementation plans exceed their timeline?
According to EHR in Practice (2024), while it’s mostly due to poor goals and planning, each implementation process varies, as one cannot find a standard EHR plan to follow.
There are often times when hospitals and other health institutions underestimate the complexity of data migration and do not train staff well.
To help in avoiding these common mistakes, this guide aims to deliver a complete, thorough, and standard EHR implementation plan, from checklists to examples.
What Is an EHR Implementation Plan and Why It Matters
An EHR implementation plan is a structured guideline that directs healthcare organizations through the whole process of deployment, data configuration, software training, and electronic health system optimization.
The whole EHR implementation process is like following a planned roadmap to deploy and optimize the use of Electronic Health Records in health institutions.
An EHR system ensures that records are inputted digitally, making healthcare access better for everyone.
A plan for health institutions to transition from manual or legacy tracking to digital records matters so that the process is smooth, regulatory compliant, and aligned with clinical and operational goals.
Why an EHR Implementation Plan Matters
- HIPAA and ONC Compliance: Ensure that your EHR and other health IT systems adhere to the standards set by HIPAA and ONC for Health Information Technology.
- Interaction Across Departments: Make sure that the plan encourages interoperability within departments and with outside providers as well.
- Enhance Patient Safety: Every plan considers the patient’s well-being. An implementation plan ensures that there is proper patient safety and care coordination.
- Accuracy and Efficiency: An EHR implementation plan guarantees that medical billings and hospital operations are done with a structure and takes into account the well-being of patients.
Small health clinics usually focus on the rapid deployment stages of EHR implementation, while large healthcare facilities mostly focus on coordination across departments within the hospital to ensure seamless execution of the EHR implementation plan.
Stages of EHR Implementation (The Four Core Phases)
Clinics, hospitals, and other health-focused institutions that implement the use of electronics in recording patient data follow a strict EHR implementation timeline.
Learn more about the four steps to a successful EHR implementation and what other things are needed to consider when following the different stages of EHR implementation.
Phase 1: Planning and Assessment
This initial phase focuses on evaluating organizational readiness, defining clear objectives, and building the strategic foundation needed for a smooth and effective EHR rollout.
As mentioned above, an EHR implementation plan is the roadmap of any healthcare facility that wishes to adapt to automating their patient record.
This phase of the stages of EHR implementation is crucial; it’s the foundation of success.
- Set SMART Goals: Define goals for your EHR implementation that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, e.g., “Reduce charting time by 30% within 4 months.”
- Define Team Roles: Identify responsible and trustworthy people who can lead the implementation process as the project manager, IT head, and administrative lead, among other important roles.
Example:
| Goal/Task | Assigned To | Due Date |
| Define Scope of Project | Project Manager | Week 1 |
| Assess Facility | Administrative Lead | Weeks 2-3 |
- Assess Facility Readiness: Evaluate the state of your healthcare facility and look into its infrastructure, digital literacy, and other operational bottlenecks that can hinder the progress of your EHR implementation plan.
- Redesign Work Operations: Look into inefficiencies in workflows. Before planning to digitize it, find out how to simplify it first.
- Pre-Select EHR Software Partners: Find providers that match your EHR implementation timeline and ask for proposals and demos. EHR providers such as Pace+ offer options tailored for behavioral health concerns.
The usual timeline of planning and assessing an EHR implementation plan usually differs in timespans depending on the size of a healthcare facility.
Small clinics usually take up to 4 to 8 weeks of planning and preparation before fully integrating EHR into their workflows, while bigger hospitals take up to 8 to 12 weeks, as they have a lot to consider.
Phase 2: System Setup, Configuration, and Data Migration
This phase is the most technical and crucial part of the EHR implementation plan. There needs to be a seamless transition from manual data to the well-formatted EHR cloud database.
- Customize EHR Data Setup: Build an EHR data stream that can be easily understood by the whole healthcare team and, therefore, easily implemented. Tailor old templates and forms, as well as user and access controls.
- Data Migration: Cleaning the data from manual to EHR data needs to be thoroughly cleaned for duplicates and other issues that may arise when running the new software.
- System Testing: It’s important to fully let healthcare staff transition to an EHR system. To achieve this, a test run of the new system is needed to educate both staff and patients on the benefits of EHR.
- Developing Contingency Plans: Feedback from employees and patients from test runs enables the creation of fallback procedures. Test these backup plans to ensure that everyone knows what to do when all else fails.
Setting up the new system, teaching everyone involved how to run it, and configuring the whole EHR implementation plan takes around 8 to 12 weeks.
It is best to start beta testing early to avoid delays when actually running your new EHR system.
Phase 3: Training and Go-Live Execution
This phase is centered on user preparation, hands-on training, and real-time deployment, ensuring that staff can confidently operate the new EHR system during live clinical use.
This phase of the EHR implementation timeline drives user adoption.
- Role-based Training: This involves the actual training of physicians, nurses, billing staff, and other health institution users who are important in the involvement in the EHR transition.
- Testing and Simulations: It’s best to test the efficiency of the EHR implementation with scenarios that test the usability of your EHR system, e.g., when a patient is asking for their billing records.
- Go-Live Execution: When running mock tests or actual tests to assess its real-world readiness, you can choose between “big-bang” testing (all-at-once) or “phased” testing (by department).
- Command Support: Be sure to provide on-site support during launch week. Project managers should always be on standby for any workflow questions.
- Reduce Patient Load: Temporarily ease the transition of the EHR implementation and accommodate only a few patients during the training and execution phase.
The timeline for training and execution is usually done 2 to 4 weeks before the EHR launch proper. Another week of full intensity support is allotted to tackle any problems that arose during the test implementation.
Phase 4: Post-Implementation Expansion
This final phase emphasizes continuous evaluation, performance monitoring, and long-term optimization to enhance system efficiency and sustain successful EHR adoption.
The EHR implementation process does not end with go-live execution. There needs to be a thorough evaluation of the whole EHR implementation process: strengths and weaknesses that should be taken care of.
- Monitor KPIs: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as billing accuracy, patient yield, and end-user adoption should be considered when assessing how successful the EHR implementation plan is.
- Receiving Feedback: Gather opinions and information regarding the overall performance of the healthcare facility when using the new EHR system. Use surveys and daily huddles to tackle issues.
- Review Work Cycles: Conduct reviews of every part of the EHR implementation plan at 3, 6, and 12 months.
- Refresher Training: Offer practices and drills that address turnover concerns and updates as well.
- Maintain Regulation Compliance: Always update and make sure that HIPAA and ONC standards are always met when conducting the EHR implementation process.
Complete EHR Implementation Plan Checklist
Now that we’ve learned about the different phases of an EHR implementation plan, what are the contents of an EHR implementation plan checklist? What does an EHR implementation plan template look like?
EHR Implementation Plan Example
Example of an EHR Plan Checklist on Phase 1: Planning and Assessment
| Phase | Task | Owner | Due Date | Status | Notes |
| 1: Planning | Define project scope. | Project Manager | Week 1 | In Progress | Aim to reduce charting time by 30%. |
| 1: Assessment | From a core team. | Project Manager | Week 2 | To be done | Assign technical concerns to a technical head. |
A cohesive EHR implementation plan is the cornerstone of every EHR rollout.
This is why every EHR implementation checklist always includes scope identification during the first phase.
Once you have established the concrete next steps in your plan, a team is needed to execute the tasks planned.
This is to ensure that everything goes smoothly and no plate is too full during the whole implementation process.
Example of an EHR Plan Checklist on Phase 2: System Setup, Configuration, and Data Migration
| Phase | Task | Owner | Due Date | Status | Notes |
| 2: System Setup | Clean Manual Data and Transfer to EHR data | IT Head | Week 4 | In Progress | Reduce repetitive data by 50%. |
| 2: Configuration | Conduct Downtime Test | IT Head and Personnel | Week 6 | To be done | Assess parts in the EHR implementation with the biggest downtime. |
By now, your EHR implementation checklist is in its second phase.
Your EHR implementation plan has now considered the project’s scope, the size of your team, and how much it would take to fully integrate EHR into the hospital’s system.
This phase determines the needs you have for an EHR system. Look into different companies that offer affordable but good-quality EHR software solutions that can enhance medical practice.
Example of an EHR Plan Checklist on Phase 3: Training and Go-Live Execution
| Phase | Task | Owner | Due Date | Status | Notes |
| 3: Training | Train all roles with their assigned task. | All system users | Week 10 | In Progress | Be ready for any questions. |
| 3: Go-Live | Go-Live Readiness | Project Manager | Week 13 | To be done | Account for downtime during go-live execution. |
Medical staff training is a crucial part of any EHR implementation plan. The training prepares medical staff to effectively transition from manual records to a fully electronic system.
Once medical trainees are already competent and comfortable in using their new EHR system, it’s time to evaluate the go-live readiness of everything.
Example of an EHR Plan Checklist on Phase 4: Post-Implementation Expansion
| Phase | Task | Owner | Due Date | Status | Notes |
| 4: Post-Implementation | Post-Go-Live KPI tracking | Administrative tracking | Week Tracking | To be done | Make KPI reports for 2 weeks of Go-Live execution. |
EHR Implementation Timeline and Example Plan
As said earlier in this blog, different factors affect an EHR implementation timeline.
Hospitals and other healthcare facilities that want to follow a certain timeline should consider variables such as size, integrations, and complexity of manual data transfer.
Here are some EHR implementation plan examples:
EHR Implementation Timeline for Small Clinics (6 Months)
Small clinics can typically complete an EHR transition within a six-month period due to their streamlined workflows, fewer departments, and lower patient volume. This condensed timeline allows providers to focus on core activities such as planning, vendor selection, setup, and staff training without disrupting daily operations. The sample timeline above illustrates how each phase progresses month-to-month, ensuring that system configuration, data migration, and go-live preparation happen in a structured and manageable sequence.

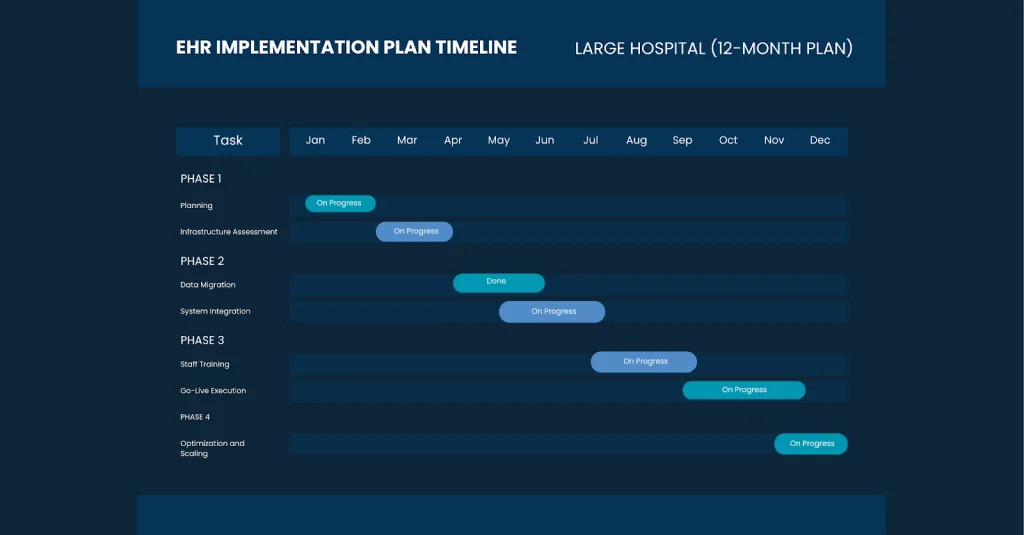
EHR Implementation Plan for Large Hospitals (12 Months)
Large hospitals generally require a longer, more structured 12-month implementation timeline due to their extensive departments, higher patient volume, and broader technology requirements. This extended schedule allows leadership teams to carefully coordinate system integrations, manage complex data migration, and train diverse clinical and administrative staff. A year-long plan also provides enough time to conduct phased rollouts, minimize workflow disruptions, and ensure that every unit—from emergency care to billing—adapts smoothly to the new EHR system.
Common EHR Implementation Plan Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
We wish to conduct a full transition to electronic health records in a very orderly and timely manner.
But we cannot escape any encounters or hazards that might derail our plans in their original timeline.
Here are some implementation pitfalls to look out for and how we can avoid them.
Inadequate Staff Training
Even when given ample time in the whole EHR implementation timeline, there can be times when training staff is not enough.
It’s best to use better-paced and role-based learning, such as real-life stimulation that can benefit not only the users but also the target audience, which is the patients.
Poor Data Migration
No matter how long and hard one cleans manual data when transitioning to electronic records, there will still be some data matches that have discrepancies.
Validate each piece of data and do testing with everyday scenarios that need patient data, such as billing or insurance claims, and prepare recovery options for standby.
Vendor Mismatch
Some EHR software solution vendors can offer promises that are too good to be true, and it turns out it’s not the best answer we are looking for.
Before settling on one EHR, score each software with a demo scoring matrix. Integrate demo testing into your EHR implementation steps, and test each option on the market.
No Downtime Plan
Take note that EHR relies on computers and cloud-based systems when looking into patient data and records; that entails downtime scenarios that are out of your hands.
Instead of dwelling on it as a problem, reverting to manual procedures is the easiest solution there is to downtime scenarios.
No Room For Change
In every work setting, some team members resist change, especially technological changes, which are harder to accept.
Better communicate the benefits of an EHR system clearly and involve team members earlier than the proposed implementation date.
Measuring Success – KPIs After Go-Live
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measures that are tracked across the EHR system to look into the performance of the implementation and ensure future optimizations are needed.
These KPIs include technicality, clinical operations efficiency, financial performance, and patient satisfaction.
Technical Performance
- Billing Accuracy and Completeness: This KPI looks at whether patient data is correct, and this is ensured through regular auditing and validation checks done by the IT team.
- Data Recovery: This looks into the EHR system’s ability to keep patient data safe from malware attacks, hackers, and data loss. In cases of system failures, data should be recovered quickly.
Clinical Operation Efficiency
- Chart Completion Rate: Tracking clinical documentation is done quickly and accurately, eliminating frequent operation bottlenecks.
- User Adoption Rate: Users should be able to use the system with ease. During the EHR implementation, every aspect of the system is easy to understand and use by everybody.
- Patient Wait Time: See improvements in the daily patient volume capacity and measure patient encounter metrics.
User and Patient Satisfaction
- Staff Satisfaction: Collect feedback from medical staff and other users to obtain actionable insights that can help improve areas lacking in the EHR implementation.
- Patient Satisfaction: Patient turnout and sentiment are also important, and we acquire them through surveys and one-on-one patient talks.
Here’s a table on KPIs, how to measure them, and how frequently they should be measured.
| Key Performance Indicator | Measurement Method | Frequency |
| Billing Accuracy and Completeness | Error Reduction, Claims Rejection Reports | Monthly |
| Data Recovery | System Downtime | Monthly |
| Chart Completion Rate | Medical Task Completion | Weekly |
| User Adoption Rate | User Logins, Task Completion | Weekly |
| Patient Wait Time | EHR Timestamps | Monthly |
| Staff Satisfaction | Surveys | Quarterly |
| Patient Satisfaction | Surveys | Quarterly |
Tip: Use these KPIs to guide you in making quarterly optimization reports and cycles.
Conclusion – Turning Planning into Long-Term Success
EHR implementation is not a one-time event; it’s a continuous journey into transforming the landscape of the medical field.
With the right planning, team members, and software tools, you can transform your practice’s efficiency, compliance, and patient satisfaction:
And remember: EHR optimization does not stop at go-live execution. Always keep on reviewing, training, and improving.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs regarding the stages of EHR Implementation:
What is the most important factor for successful EHR implementation?
Electronic Health Record (EHR) software is a digital system that stores, organizes, and shares patient information securely in one place. It replaces paper charts, prevents files from being lost, and allows clinics and hospitals to access records safely. This makes healthcare smoother, faster, and less confusing for both providers and patients.
How is EHR different from EMR?
An Electronic Medical Record (EMR) is a digital version of a patient’s chart used within one practice, while an Electronic Health Records (EHR) is designed to be shared across multiple healthcare providers. An EHR follows the patient, connecting doctors, hospitals, and specialists so everyone can see the same information.
What are the main features of an Electronic Health Record (EHR)?
The main features of an EHR software are charting tools, practice management functions, patient portals, and sometimes built-in telehealth. These features help doctors and patients communicate effectively and keep track of care without unnecessary hassle.
How much does it cost?
The cost of EHR really depends. Small clinics can get simpler systems that don’t cost much. Big hospitals usually need more complicated setups and, yeah, they’re pricier.



