Medical billing is the process of translating clinical services into billable claims to ensure accurate provider reimbursement and financial compliance. This administrative function connects patient care with the revenue cycle, safeguarding the financial health of healthcare organizations.
Accurate medical billing is essential for smooth cash flow, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability. Providers rely on it for timely reimbursement, patients benefit from understandable statements, and payers use it to evaluate and process claims efficiently.
This article provides a step-by-step walkthrough of the full medical billing cycle, from the first patient encounter to final payment, while sharing best practices to improve accuracy, speed, and operational efficiency. Whether you are a healthcare professional or want to better understand your billing process, this guide offers a clear and practical overview of medical billing.
Key Components of the Medical Billing Process
Medical billing might sound like a linear process that is very straightforward. In reality, it is composed of multiple related steps that heavily rely on one another for it to work. Every stage passes information to the next, so if something goes wrong early on, the problem will build up as the steps move further.
When the workflow is healthy, claims move quickly, payments arrive on schedule, and patients get clear, understandable bills. However, when one piece of the process fails, maybe because a document is missing or a code gets overlooked, it can cause a major slowdown. This leads to delayed payments, more claim denials, extra work for staff correcting mistakes, and a lot of frustration for patients.
Getting a handle on medical billing means knowing the system inside and out, how it affects your income, your patients, and what you can do to fix it. Let’s talk through it.
1. Patient Registration & Insurance Verification
Patient Registration & Insurance Verification is the first step in the medical billing process and lays the groundwork for accurate claim submission. During this stage, patient demographic information and insurance coverage details are collected and validated to confirm eligibility and financial responsibility. Completing this process correctly ensures that services are billed to the correct payer, required authorizations are identified early, and preventable claim denials are avoided.
Every billing cycle begins long before a claim ever reaches an insurance company. It starts the moment a patient schedules an appointment.
What happens here?
- Recording patient demographics (name, date of birth, address
- Collecting insurance details like member ID, group number, and payer information
- Confirming copay, coinsurance, and deductibles
- Identifying whether authorization or referrals are needed
- Reviewing plan limitations or exclusions
Insurance verification is one of the most crucial stages in the cycle. One simple mistake an outdated policy number or inactive plan, for instance, can cause the claim to be rejected later on. There are so many practices that lose thousands of dollars a year because of errors that are not caught early on.
Verifying coverage upfront not only reduces denials but also sets proper expectations for the patient regarding their financial responsibility.
2. Medical Documentation Collection
Medical Documentation Collection is the process of recording complete and accurate clinical details from the patient encounter to support billing. Providers document diagnoses, procedures, and treatment decisions, which billers and coders use to create compliant and billable claims. Proper documentation ensures services are justified, coded correctly, and eligible for reimbursement.
When the patient encounter starts, the provider becomes an important contributor to the billing process. The billers and coders use the documentation such as the procedures and treatments recorded by the provider, to create an accurate insurance claim.
Key requirements include:
- Clear notes describing the patient’s symptoms, findings, diagnoses, and treatment
- Accurate time documentation for time-based services
- Supporting clinical documents such as test results or referrals
- Compliance with payer documentation standards
Documentation must paint a complete picture of the encounter. Even if a service was performed, it cannot be billed unless it is clearly documented. Ambiguous notes can result in downcoding, payer audits, or total loss of reimbursement.
Thorough documentation ensures that coding is accurate and claim submission moves forward without delays.
3. Charge Entry
Charge Entry is the process of converting documented medical services into standardized billing codes for claim submission. During this stage, procedures, diagnoses, and modifiers are accurately assigned to reflect the care provided and meet payer requirements. Precise charge entry ensures claims are complete, compliant, and ready for smooth processing without unnecessary delays or denials.
This includes:
- Applying CPT and HCPCS codes to describe procedures
- Linking appropriate ICD-10 diagnosis codes
- Assigning modifiers to clarify services
- Setting charges based on fee schedules
- Reviewing provider documentation for clarity
Accurate coding is the backbone of successful billing. Even a small mistake, such as a missing modifier or incorrect diagnosis code, can trigger an automatic denial. Coders must stay up-to-date with constantly evolving guidelines, payer rules, and new or removed codes. Charge entry mistakes create expensive bottlenecks. On the other hand, well-executed coding ensures claims pass through the system smoothly.
4. Claim Scrubbing & Compliance Checks
Claim Scrubbing & Compliance Checks involve reviewing claims for errors, inconsistencies, and rule violations before submission. This step ensures that coding, modifiers, and medical necessity align with payer and regulatory requirements. Proper scrubbing increases clean claim rates, reduces rejections, and supports faster reimbursement.
Typical scrubbing activities:
- Checking for missing information
- Running NCCI (National Correct Coding Initiative) edits
- Verifying modifier usage
- Ensuring diagnoses support medical necessity
- Checking for bundling or unbundling issues
- Validating payer-specific rules
Automated scrubbing tools catch errors in seconds that might take humans hours to identify. Manual review is still important, especially for complicated claims, but automation dramatically increases clean claim rates.
A well-scrubbed claim reduces rejections, accelerates payment, and improves revenue cycle performance.
5. Claim Submission
Claim Submission is the process of sending error-free claims to the payer for reimbursement. Prompt submission ensures timely payment and keeps the revenue cycle moving smoothly.
Common submission methods include:
- Through a clearinghouse (most common)
- Direct submission to the payer
- Via EDI formats (837P for professional and 837I for institutional claims)
The submission speed is essential to payment timelines. Submissions that are delayed can push claims outside filing limits, making reimbursement impossible. Submitting claims promptly is one of the easiest ways to improve cash flow.
6. Payer Adjudication & Response
Payer Adjudication & Response is when the insurance company reviews a submitted claim to determine payment eligibility. The payer then sends an EOB or ERA, showing what was paid, denied, or assigned to the patient.
What payers review:
- Whether the service was medically necessary
- If the provider was in-network
- Whether coverage was active
- If documentation supports the codes
- Whether the claim follows their payment policies
After evaluation, the payer sends an:
- EOB (Explanation of Benefits) for patients.
- ERA (Electronic Remittance Advice) for providers.
The ERA is responsible for explaining how much was paid, denied, reduced, or dedicated under a patient responsibility. Tracking adjudication can help identify recurring problems such as underpayments or recurring denials from the same payer.
7. Denial Management & Appeals
Denial Management & Appeals addresses claims that are denied by the payer, identifying and correcting the reasons for rejection. Effective management and timely appeals help recover rightful revenue and maintain cash flow.
Common denial reasons:
- Incorrect or missing codes
- Lack of medical necessity
- Invalid insurance details
- Authorization not obtained
- Missing documentation
- Duplicate claims
Effective denial management includes:
- Reviewing denial reasons
- Identifying the exact cause
- Correcting the issue
- Resubmitting the claim within the allowed timeframe
- Filing appeals for claim reconsideration
A denial management system that is proven and developed ensures that practices do not lose revenue for services they rightfully provided.
8. Patient Billing & Collections
Patient Billing & Collections involves notifying patients of their remaining balance and facilitating payment. Clear communication and transparent statements help ensure timely payments and reduce confusion.
This stage involves:
- Sending detailed statements.
- Breaking down insurance payments and patient portions.
- Offering payment plans
- Following up on unpaid balances
- Handling disputes or questions
- Initiating collections when necessary
Patients are usually confused about their healthcare costs; that is why clear and healthy communication is important. Patients appreciate transparency about what they need to pay, why they need to pay it, and how they can pay for it.
9. Payment Posting & Revenue Reconciliation
Payment Posting & Revenue Reconciliation records insurer and patient payments in the system and applies necessary adjustments. This ensures accurate revenue tracking, identifies discrepancies, and supports reliable financial reporting.
This includes:
- Posting insurer payments from ERAs
- Recording patient payments
- Applying contractual adjustments
- Identifying unpaid or underpaid claims
Revenue Reconciliation: Expected vs. Actual
For a financial report to reflect true revenue and for every payment to be accounted for, precise payment posting is essential. It is also a key tool for identifying payer underpayments, coding inaccuracies, and gaps in your workflow.
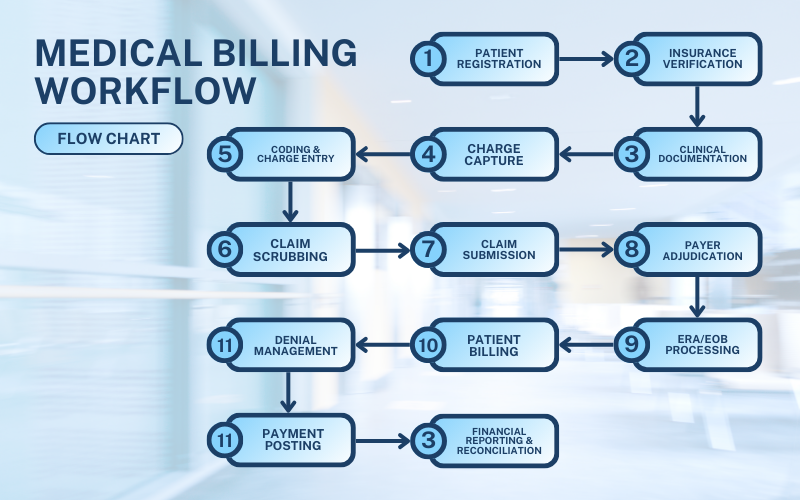
Full-Cycle Medical Billing Workflow (Visual + Step-by-Step)
To understand how everything comes together, here’s the complete workflow:
Common Areas Where Medical Billing Errors Occur
Medical billing errors typically arise in specific stages of the claims process, impacting reimbursement, compliance, and revenue cycle efficiency. The most frequent errors include:
- Incorrect patient insurance details
- Incomplete or vague documentation
- Coding mistakes, such as incorrect modifiers or mismatched diagnoses
- Missed prior authorization requirements
- Delayed responses to claim denials
- Inaccurate payment posting
Example scenario:
Picture a patient visiting their doctor for a routine follow-up. The provider orders a diagnostic test but doesn’t fully document the supporting diagnosis. As a result, the insurance company denies the claim, labeling the service as “not medically necessary.” The billing team then has to go back to the provider for clarification, correct the codes, and resubmit the claim, delaying payment by several weeks.
Common Challenges in Medical Billing
Medical billing remains a complex process despite automation, advanced billing software, and digital tools. Each claim must comply with coding updates, payer-specific rules, and strict documentation standards to ensure accurate reimbursement.
No two insurance companies operate the same way, requiring billers to stay alert to variations in coverage, medical necessity guidelines, and submission deadlines. Even small mistakes, such as typos, outdated codes, or missing referrals, can trigger claim denials or payment delays.
Although technology improves efficiency, human judgment and manual review are still essential for accurate claims processing and smooth revenue cycle management.
Frequent Challenges in Medical Billing
Frequent challenges in medical billing disrupt claim accuracy and slow revenue cycles. The most common issues include:
- Incomplete or inconsistent documentation
- Coding or charge entry errors
- Eligibility issues discovered after services are rendered
- Slow payer processing times
- Increased scrutiny of high-cost procedures by payers
- Regulatory changes requiring ongoing staff training
- Claims denied due to missing prior authorizations
These challenges often result in longer A/R days, cash-flow delays, and administrative burnout.
Best Practices for Effective Medical Billing
It requires consistent effort to improve billing performance, as well as proper training, and a real focus on quality. When staff stay updated, follow clear processes, and pay attention to details, the entire billing workflow becomes smoother, more accurate, and far more reliable.
1. Accurate and Timely Documentation
Providers should aim to document every encounter as soon as possible. Delayed documentation increases the risk of missing details and coding errors.
Best practices include:
- Using structured templates
- Standardizing documentation formats across providers
- Asking clarifying questions early
- Implementing documentation improvement programs
Good documentation is the foundation of clean claims.
2. Regular Staff Training
Billing and coding rules are constantly changing, that is why even small updates can have a huge effect on reimbursement. To prevent costly mistakes, lessen denials, and ensure that each claim is submitted correctly the first time.
Training should cover:
- Annual CPT and ICD-10 updates
- Modifier and bundling rule changes
- Medicare and Medicaid guidelines
- Payer-specific updates
- Audit findings and recurring team errors
Ongoing education reduces denials and keeps billing teams confident and competent.
3. Use of Technology
With the presence of technology in helping to boost billing accuracy, it reduces manual data entry, flagging possible errors, and streamlining claim submission. With automated eligibility checks, real-time claim scrubbing, and integrated EHR systems, billing teams can work faster, avoid oversights, and maintain consistent, high-quality results.
Helpful tools include:
- Automated claim scrubbers
- Integrated EHR and billing systems
- Charge capture tools
- Real-time eligibility verification
- Analytics and reporting dashboards
Automation reduces manual errors and frees staff to focus on high-value tasks.
4. Denial Prevention and Management
It is vital to identify first the root causes of denials in order to prevent it, ensuring a strong documentation, and making sure that every claim meets the payer requirements before it is ever submitted.
Strong denial prevention includes:
- Identifying common denial trends
- Auditing documentation and coding regularly
- Using checklists for authorization and referrals
- Implementing standard workflows for appeals
In order for revenue to recover quickly, practices should take denial prevention seriously.
5. Streamlined Patient Communication
In order for patients to pay their bills, they need first to understand them; that is why it is crucial for the statements to be clear, easy to read, and backed up by simple explanations. Transparency promotes trust, lessens confusion, and encourages quick, more consistent payments from patients.
Effective communication includes:
- Clear, jargon-free statements
- Transparent billing breakdowns
- Digital payment options
- Automated reminders
- Financial assistance counseling
Good communication improves both collections and patient satisfaction.
How to Improve Your Medical Billing Process
Improving the medical billing process requires targeted strategies that enhance accuracy, reduce denials, and streamline the revenue cycle. Key approaches include:
1. Leverage Technology (AI, RPA, Automation)
Automation tools reduce manual errors and improve billing efficiency. Examples include:
- AI tools that predict claim denials
- RPA bots for repetitive tasks, such as posting ERAs
- Automated eligibility verification
- Intelligent charge capture tools
- Predictive analytics to identify revenue risks
2. Monitor Key Revenue Cycle KPIs
Measuring critical KPIs enables organizations to detect performance issues early.
Important metrics include:
- Clean Claim Rate
- Denial Rate
- Days in Accounts Receivable
Net Collection Rate - Charge Lag Time
- First Pass Resolution Rate (FPRR)
3. Conduct Regular Internal Audits
Internal audits refine billing processes and prevent financial loss.
Audit focus areas include:
- Coding accuracy
- Documentation completeness
- Underpayments
- Contract compliance
- Common denial reasons
4. Improve Provider–Coder–Biller Communication
Effective communication among providers, coders, and billers reduces errors and increases efficiency.
Strategies include:
- Sharing coding feedback with providers
- Holding weekly communication huddles
- Establishing clear documentation expectations
- Using performance dashboards
5. Enhance Patient Experience and Transparency
Transparent and patient-friendly billing minimizes confusion and builds trust.
Best practices include:
- Offering cost estimates before visits
- Providing easy-to-read statements
- Allowing multiple payment options
- Offering financial counseling
- Using patient-friendly language
Medical Billing Services Explained
Medical billing services manage the process of converting healthcare services into accurate claims and reimbursements, either through in-house teams or outsourced partners. Each model has distinct advantages and limitations depending on organizational needs, scale, and resources.
In-House Medical Billing
In-house medical billing is managed internally by the healthcare organization using its own staff and systems.
Pros:
- Full control over billing processes
- Immediate access to billing data
- Direct communication with providers and staff
Cons:
- Ongoing staff training requirements
- Higher overhead and operational costs
- Increased administrative responsibility
Outsourced Medical Billing
Outsourced medical billing is handled by an external billing service provider on behalf of the healthcare organization.
Pros:
- Access to experienced medical billing specialists
- Improved denial management processes
- More consistent reimbursement outcomes
- Reduced administrative workload
Cons:
- Limited direct operational oversight
- Dependence on communication with the billing partner
Typical Medical Billing Services
Medical billing services commonly include the following operational functions:
- Medical coding
- Claim preparation and submission
- Denial management and appeals
- Payment posting and reconciliation
- Patient billing and statements
- Revenue reporting and analytics
Benefits of an Optimized Medical Billing Process
An optimized medical billing process improves reimbursement accuracy, reduces claim denials, and strengthens overall revenue cycle performance. When billing workflows are efficient and standardized, the entire healthcare organization benefits operationally and financially.
The key benefits of an optimized medical billing process include:
- Faster payments due to clean and accurate claim submission
- Reduced claim denials through proper coding, documentation, and payer rule adherence
- Improved cash flow with shorter reimbursement cycles
- Fewer patient billing disputes caused by clearer and more accurate statements
- Increased patient trust through transparent and consistent billing practices
- More staff time for patient care as administrative rework decreases
A well-managed medical billing process directly supports long-term practice stability by protecting revenue, improving patient satisfaction, and reducing operational strain.
Conclusion
Medical billing is a core function of the healthcare revenue cycle that ensures accurate reimbursement, fair patient billing, and compliant claim processing. When medical billing processes are executed correctly, organizations experience faster payments, fewer claim denials, improved operational efficiency, and stronger financial stability.
Improving medical billing outcomes requires accurate documentation, effective use of technology, consistent communication across teams, and regular performance monitoring. These practices reduce errors, streamline workflows, and prevent avoidable revenue loss. Efficient billing processes also improve the patient experience by minimizing confusion and billing-related disputes.
Healthcare organizations that proactively evaluate and optimize their medical billing workflows are better positioned to maintain a stable, sustainable revenue cycle. Strengthening billing accuracy and efficiency supports long-term growth while reducing administrative burden across the practice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is medical billing, and why is it important?
Medical billing is the process of submitting claims to insurers for payment. It ensures providers receive reimbursement for services delivered.
What are the main steps in the medical billing process?
Registration, documentation, coding, claim scrubbing, submission, adjudication, posting, patient billing, and denial management.
How does full-cycle medical billing work?
It includes everything from the first patient interaction to the final payment posting and reconciliation.
What are common mistakes in medical billing?
Incorrect codes, incomplete documentation, missed authorizations, and eligibility errors.
How can healthcare providers improve their billing process?
By improving how documentation is handled, using smart automation tools, investing in staff development, and putting solid denial-prevention practices in place, organizations can create a much smoother and more reliable billing process.
What role does technology play in medical billing?
Technology improves accuracy, speeds up workflows, reduces errors, and increases clean claim rates.
What is the difference between in-house and outsourced billing services?
In-house is managed internally, while outsourced billing uses third-party specialists.
How do billing errors affect revenue and patient satisfaction?
Errors cause denials, delays, lost revenue, and patient dissatisfaction.
How long does medical billing take?
Most claims take 7–30 days, depending on the payer and complexity.
10. What are the best practices for effective medical billing?
Timely documentation, automation, consistent training, and clear patient communication.